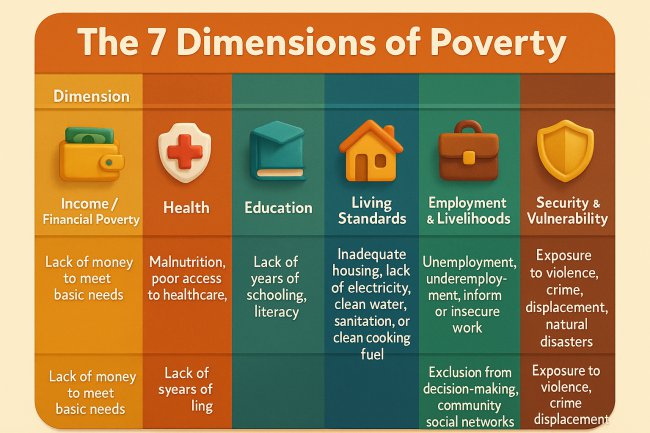
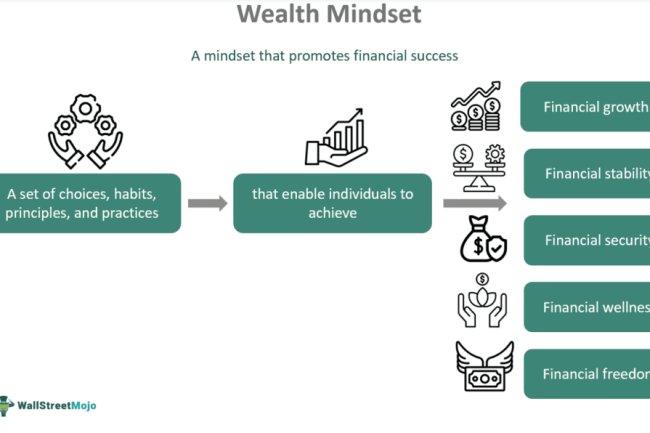
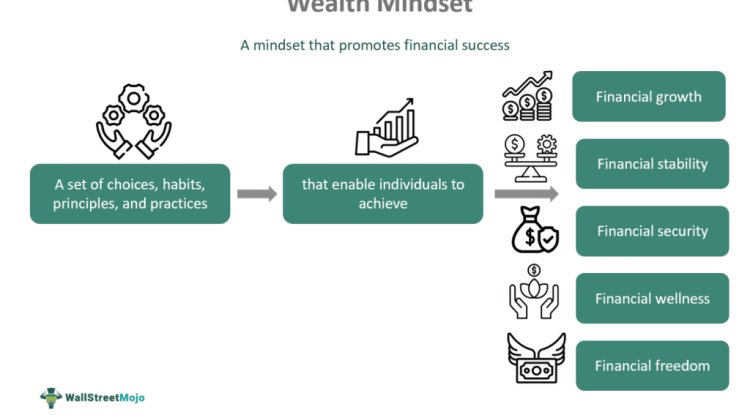
Mastering Personal Finance: The Foundation of Financial Freedom
Discover the ultimate personal finance guide covering budgeting, saving, debt management, investing, taxes, retirement, and financial literacy. Learn practical strategies to build wealth and achieve long-term financial independence.

Personal finance is the strategic process of managing your money effectively to meet your life goals. It encompasses everything from budgeting and saving to investing and retirement planning. While many focus on earning more, the real key to financial freedom lies in how well you manage what you already earn. This article explores in depth the foundational pillars of personal finance, practical tools, and lifelong strategies to help you achieve true financial independence.
1. The Philosophy of Financial Independence
Financial independence isn't just about accumulating wealth—it's about having control over your time and choices. The mindset shift required is critical. Most people work for money their entire lives, but those who achieve financial freedom make money work for them.
Key Concepts:
-
Living below your means
-
Prioritizing long-term security over short-term gratification
-
Building sustainable habits over quick fixes
Your financial journey begins with accepting responsibility for your financial future, regardless of your current situation.
2. Budgeting: Your Financial Compass
Budgeting is the cornerstone of all personal finance. It gives you a clear understanding of your income and expenses, helping you make informed decisions.
Popular Budgeting Methods:
-
50/30/20 Rule: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings/debt repayment
-
Zero-Based Budgeting: Every dollar has a job, and expenses are matched to income
-
Envelope System: Cash allocation into different envelopes/categories
Tips for Effective Budgeting:
-
Track all income sources (salary, business, passive income)
-
Categorize spending into essentials and non-essentials
-
Use budgeting tools/apps like Mint, YNAB, or Excel templates
3. Building an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a non-negotiable in personal finance. It shields you from financial shocks such as medical emergencies, car breakdowns, or sudden job loss.
How to Build It:
-
Start small: Aim for at least one month of expenses
-
Gradually build up to 3–6 months of expenses
-
Store funds in a high-yield savings or money market account
Why It Matters:
-
Prevents accumulation of high-interest debt
-
Provides peace of mind
-
Helps maintain investment strategy during emergencies
4. Debt Management and Elimination
Debt can either be a tool or a trap. Learning to manage and eliminate bad debt is essential to financial well-being.
Types of Debt:
-
Good debt: Student loans, mortgage (can increase net worth)
-
Bad debt: Credit cards, payday loans (high-interest, consumer-based)
Debt Reduction Strategies:
-
Snowball Method: Pay smallest debts first
-
Avalanche Method: Pay highest-interest debts first
-
Negotiate lower interest rates
-
Avoid taking new debt during the repayment phase
Debt Warning Signs:
-
Using credit to pay for essentials
-
Only making minimum payments
-
Hiding debt from family
5. Saving: Pay Yourself First
Saving is more than setting aside leftover money—it’s a deliberate act of prioritizing your future.
Types of Savings Goals:
-
Short-term: Emergency fund, vacation, car repair
-
Medium-term: Home deposit, education
-
Long-term: Retirement, investments
Smart Saving Habits:
-
Automate savings transfers
-
Open multiple savings accounts for different goals
-
Avoid tapping into savings for non-emergencies
6. Understanding Taxes and Legal Deductions
A basic understanding of how taxation works can save you thousands over a lifetime.
What You Should Know:
-
Income tax brackets and thresholds
-
Tax-deductible expenses (pension contributions, charitable donations)
-
How to file returns accurately and on time
-
Understand VAT, capital gains, and property taxes
Pro Tip: Consider consulting a tax advisor annually to optimize your deductions.
7. Investing: Make Your Money Work for You
Investing allows your money to grow passively, beating inflation and creating long-term wealth.
Investment Vehicles:
-
Stocks and bonds
-
Real estate
-
Mutual funds and ETFs
-
SACCOs and unit trusts (in Kenya)
Principles of Investing:
-
Start early to benefit from compounding
-
Diversify to manage risk
-
Stay consistent through market ups and downs
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
-
Chasing high returns without research
-
Timing the market
-
Investing money needed in the short term
8. Retirement Planning
Retirement may seem distant, but the earlier you plan, the more secure your future becomes.
Steps to Prepare:
-
Calculate how much you’ll need in retirement
-
Contribute regularly to pension schemes (e.g., NSSF, private plans)
-
Explore individual retirement accounts (IRAs, Personal Pension Plans)
The Power of Compound Interest:
Saving even small amounts early can grow into significant wealth over decades.
9. Insurance: Your Financial Safety Net
Insurance protects your financial progress from being wiped out by unexpected events.
Types to Consider:
-
Health insurance
-
Life insurance
-
Auto insurance
-
Property and home insurance
Key Considerations:
-
Don’t over-insure or under-insure
-
Review your policies annually
-
Always read the fine print on exclusions
10. Financial Literacy and Continuous Learning
Money management is a lifelong learning process. Staying informed helps you adapt to economic changes and new opportunities.
Ways to Stay Educated:
-
Read personal finance books and blogs
-
Attend financial webinars and courses
-
Follow reputable finance influencers and institutions
Recommended Books:
-
"Rich Dad Poor Dad" by Robert Kiyosaki
-
"The Psychology of Money" by Morgan Housel
-
"Your Money or Your Life" by Vicki Robin
11. Family and Money: Financial Harmony
Money is a common cause of stress in relationships. Open and honest communication is crucial.
Tips for Couples and Families:
-
Discuss financial goals together
-
Create joint and personal budgets
-
Teach kids about money early (allowances, saving goals)
Legacy Planning:
-
Create a will
-
Discuss inheritance plans
-
Set up trusts for minors
12. Common Financial Pitfalls to Avoid
Watch Out For:
-
Lifestyle inflation (spending more as you earn more)
-
Financial procrastination
-
Living without a budget
-
Not having a financial advisor or mentor
Avoiding these pitfalls early can save years of financial hardship.
13. Tools and Apps to Help You Stay on Track
Budgeting & Expense Tracking: Mint, YNAB, PocketGuard
Saving & Investment: PiggyVest, Cowrywise, Robinhood
Debt Management: Debt Payoff Planner, Tally
Use Technology Wisely:
-
Set alerts for bill due dates
-
Automate savings and investments
-
Monitor your credit score regularly
Conclusion
Mastering personal finance is a journey, not a destination. It requires discipline, intentionality, and continuous improvement. The goal is not just to accumulate wealth but to use money as a tool to build a life of freedom, purpose, and peace.
Whether you're paying off debt, saving for your first home, or preparing for retirement, the principles outlined in this guide will help you lay a solid foundation. Start today—your financial freedom is within reach.
Suggested Reading:
-
"The Millionaire Next Door" by Thomas J. Stanley
-
"I Will Teach You to Be Rich" by Ramit Sethi
-
"Think and Grow Rich" by Napoleon Hill
#PersonalFinance #MoneyManagement #Budgeting #SavingTips #DebtFreeJourney #EmergencyFund #TaxTips #SmartMoneyMoves #WealthBuilding #FinancialIndependence #FinancialLiteracy #InvestingBasics #RetirementPlanning #InsuranceMatters
What's Your Reaction?