DEBT MANAGEMENT: CREDIT CONTROL, LOAN REPAYMENT STRATEGIES & HOW TO BREAK THE DEBT CYCLE
Discover the ultimate guide to debt management, including practical strategies for credit control, loan repayment, budgeting, interest reduction, and breaking long-standing debt cycles. Perfect for beginners, professionals, and anyone seeking financial freedom. Learn how to regain control of your money and build long-term wealth.

INTRODUCTION: WHY DEBT MANAGEMENT MATTERS MORE THAN EVER
Debt has become one of the defining financial challenges of the 21st century. In Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, the US, and globally, millions of people are trapped in a cycle of borrowing, repaying, and re-borrowing—not because they are irresponsible, but because the financial system, consumer environment, and economic pressures make it easy to fall into debt and difficult to climb out.
The truth about debt is simple:
Debt itself is not the enemy. Poor debt management is.
Used wisely, debt can be a tool for growth—business loans, mortgages, student loans, or asset financing can accelerate progress. But used carelessly, or during emergencies without a plan, debt becomes a trap that consumes income, kills growth, and creates long-term financial paralysis.
This guide takes you step-by-step through:
• Understanding how debt works
• How to take control of credit
• Smart repayment strategies
• How to break free from the debt cycle permanently
• How to rebuild a strong financial foundation after debt
Whether you are a beginner or already earning a salary, this is your blueprint to financial control.
SECTION 1: UNDERSTANDING DEBT – THE REAL TRUTH MOST PEOPLE NEVER LEARN
Debt is not just a financial issue; it is behavioural, emotional, and psychological. Before managing debt, you must understand what it is and how it affects your entire financial ecosystem.
1.1 What Debt Really Is
Debt is money borrowed today with the promise to repay in the future, usually with interest. But beneath that definition lies a deeper truth:
Debt is the future pulling you forward.
Your future income is being consumed today.
Every loan is a commitment against your future productivity.
1.2 Good Debt vs Bad Debt
Not all debt is harmful. Some debt accelerates growth.
Good Debt includes:
• Education loans that increase earning ability
• Business loans that generate revenue
• Mortgages that build equity
• Asset financing (cars, machinery) when they create income
Bad Debt includes:
• High-interest loans (mobile loans, credit cards, shylock loans)
• Loans taken for lifestyle upgrades
• Borrowing to impress, not to progress
• Debt used for consumption rather than production
1.3 The Psychology of Debt
Debt affects:
• Sleep
• Focus
• Confidence
• Relationships
• Long-term planning
People stuck in debt experience “financial fog”—a mental state where money decisions become reactive instead of strategic.
SECTION 2: CREDIT CONTROL – HOW TO TAKE FULL CHARGE OF YOUR BORROWING POWER
Credit control means managing your borrowing behaviour before the debt even happens.
2.1 Know Your Credit Score (CRB / Credit Bureau)
Your credit score determines:
• Whether you can borrow
• The interest you pay
• Your loan limit
• Your financial reputation
Always check your credit report annually.
2.2 The 30% Rule of Borrowing
Never take debt that consumes more than 30% of your net income. Beyond that, the risk of default increases dramatically.
2.3 Avoid High-Interest Loans at All Costs
Digital loans, Fuliza, high-interest credit cards, shylock lending, and loan sharks are financial traps.
2.4 Build an Emergency Fund Before Borrowing
An emergency fund prevents you from running to loans after small crises.
2.5 Avoid Lifestyle Inflation
The moment income increases, people upgrade lifestyle—new phone, new apartment, new expenses. This creates long-term debt pressure.
SECTION 3: LOAN REPAYMENT STRATEGIES THAT ACTUALLY WORK
3.1 The Debt Snowball Method
Pay the smallest debts first to gain momentum.
This method builds psychological victory.
3.2 The Debt Avalanche Method
Pay the highest-interest debt first.
This method saves the most money in interest.
3.3 The Consolidation Method
Combine multiple debts into one manageable repayment.
Useful when:
• You have several high-interest loans
• Cash flow is strained
• You want a structured repayment plan
3.4 Refinancing
Renegotiate loan terms for:
• Lower interest
• Longer repayment period
• Reduced monthly stress
3.5 The 15% Increase Rule
Whenever income increases, raise debt repayment by at least 15% instead of increasing lifestyle.
3.6 Automate Repayments
Automation prevents missed payments—which reduce credit scores.
3.7 Use Windfalls Strategically
Bonuses, tax refunds, overtime income:
• 50% to debt
• 30% to savings
• 20% to lifestyle
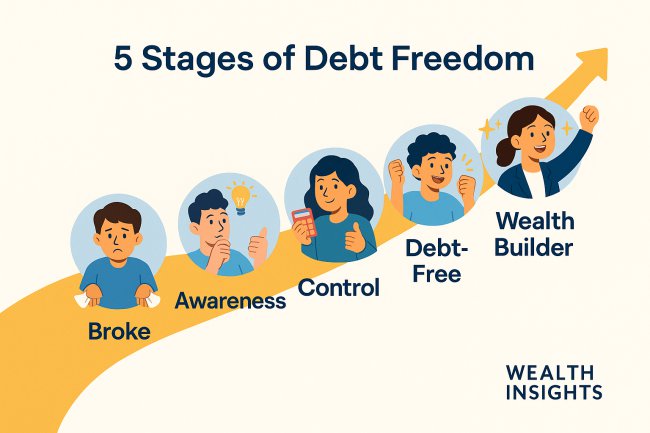
SECTION 4: HOW TO BREAK THE DEBT CYCLE PERMANENTLY
Getting out of debt is one thing; staying out of debt is another.
4.1 Identify the Root Cause of Your Debt
Most people’s root cause is one of the following:
• Emergency expenses
• Low income
• Lifestyle inflation
• Poor planning
• Impulse buying
• Lack of financial discipline
• Giving out money without strategy
• Borrowing to impress
4.2 Create a Zero-Based Budget
Every shilling must have an assignment.
No free-floating money.
4.3 Build the Three Essential Financial Buffers
-
Emergency Fund (3–6 months expenses)
-
Sinking Funds (school fees, rent, annual expenses)
-
Opportunity Fund (investments and rare opportunities)
4.4 Destroy High-Interest Debt First
It grows fastest and eats wealth silently.
4.5 Stop Taking New Debt During Repayment
Debt stacking makes repayment almost impossible.
4.6 Increase Income to Escape Faster
No one becomes debt-free by cutting expenses alone.
Increasing income accelerates repayment.
Ways include:
• Freelancing
• Selling skills
• Online business
• Commission jobs
• Consulting
• Content creation
• Side hustles
4.7 Build Better Financial Habits
Without changing habits, debt freedom is temporary.
SECTION 5: REBUILDING YOUR FINANCIAL FUTURE AFTER DEBT
5.1 Rebuild Your Credit Score
• Pay all bills on time
• Keep credit usage below 30%
• Avoid too many loan applications
• Monitor your credit report
5.2 Start Investing Early
After debt freedom:
• Start with low-risk investments
• Automate monthly contributions
• Build wealth through consistency
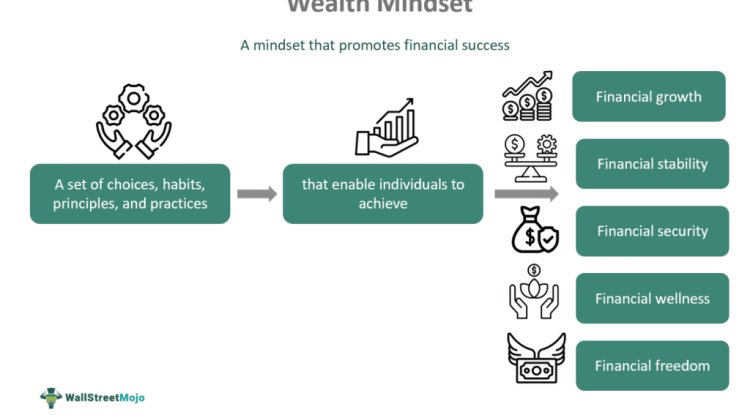
5.3 Adopt a Wealth Mindset
• Think long-term
• Avoid impulse decisions
• Prioritize value creation
• Delay gratification
• Protect income streams
SECTION 6: WHEN DEBT BECOMES A CRISIS – HOW TO SEEK HELP
If debt is overwhelming:
• Talk to your bank
• Request restructuring
• Seek financial counseling
• Join savings groups (SACCO)
• Consider refinancing
• Get accountability support
CONCLUSION
Debt does not define you. It is simply a financial condition that can be reversed with:
• Knowledge
• Discipline
• Strategy
• A long-term plan
When you master credit control, implement smart repayment strategies, and build buffers that prevent future borrowing, you unlock the door to financial freedom. Debt management is not about struggle; it is about strategy.
With the right systems, anyone—from beginners to working professionals—can break the debt cycle and build lasting wealth.
What's Your Reaction?